
some show the stats in a nice dashboard style.Some of them allow you to set up alerts.I'm going to include a bunch of tools and services that you can use to monitor your servers.
#Linux terminal process monitor install
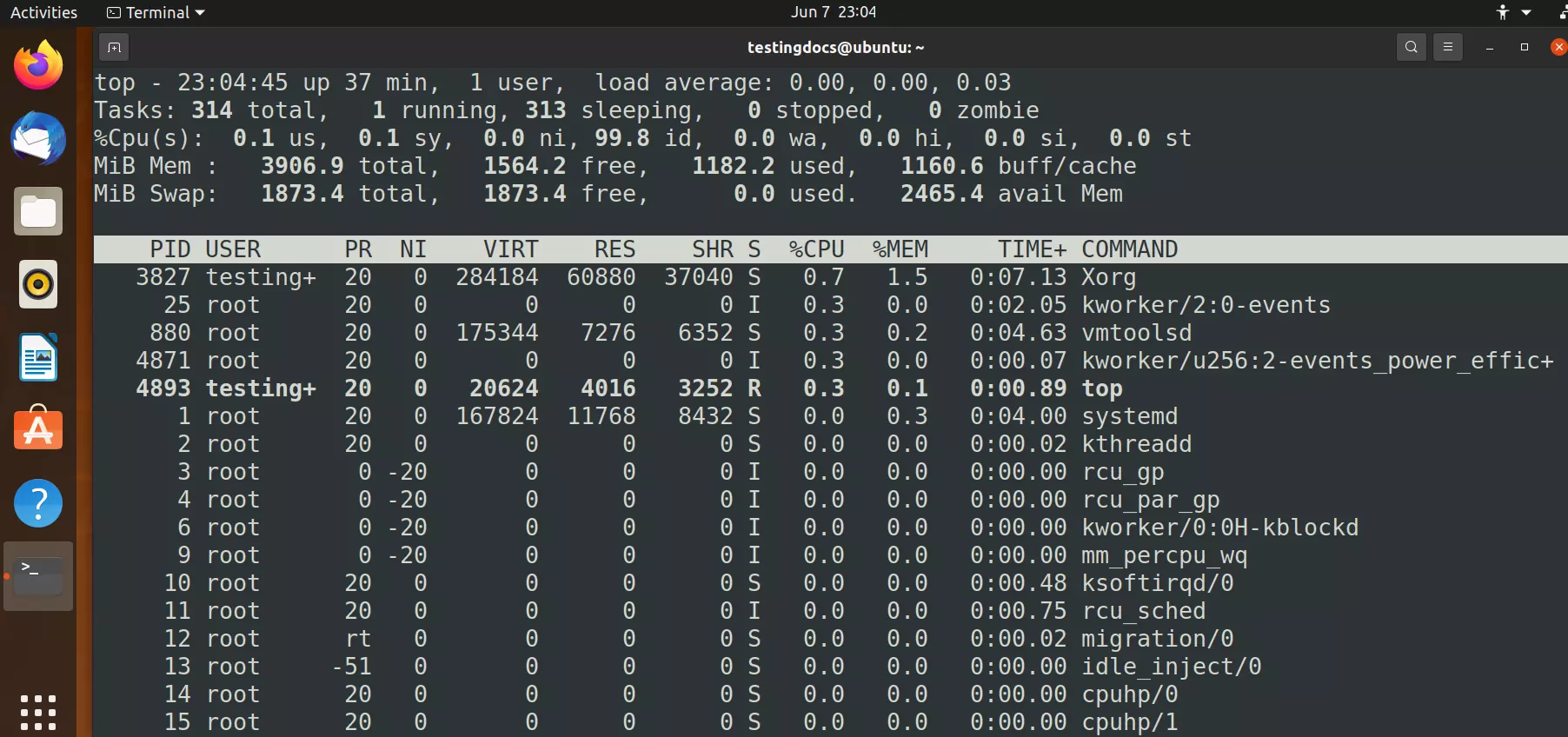
This is why it is essential to install dedicated DevOps monitoring tools to ensure efficient maintenance and monitoring. If your server runs out of disk space, the running services will be affected. If you know what's going on with your servers, you could avoid potentially catastrophic situations. Monitoring the servers is also crucial to maintain them effectively in long run. To learn more about its extensive usage options, run man htop on your Linux terminal.It's just not enough to deploy a specifically configured Linux server. Htop is a flexible Linux tool for process viewing, process management, and system control as you do not have to memorize any terminal commands for managing or viewing targeted processes. Kill Linux Processīefore confirming your KILL decision by hitting on your keyboard, you will have other send signal options apart from SIGKILL (kill a process signal) as depicted by the above screen capture. With the F9 function key, you can kill any highlighted running process that might be affecting the health of your operating system. You will be able to know if it is active or inactive. Sort Linux Processį3 function key lets you search for a specific process. List Linux Process InformationĪs for the function keys highlighted at the bottom of the screen capture ( F1 to F10), the F6 function key, for instance, gives you some flexibility on how your processes should be displayed. The bottom section of the Htop interface represented by the screen capture below highlights other important process-related information such as PID (Process id), USER (owner of the process), PRI (Process Priority), RES (Resources used by the process), CPU% (CPU percentage allocated for the execution of the process), and MEM% (main memory or RAM used by the process). Threads ( thr) represent sequential tasks that a single highlighted process can handle. You will be met with an interface similar to the above screen capture, where htop provides very detailed information about your Linux system.įor instance, the screen capture above reveals critical information on the main memory/RAM (Mem) usage, Swap memory (Swap) usage, and Tasks together with their total and active threads (thr) of a highlighted process (In blue). $ sudo emerge sys-process/htop Īfter Htop has successfully installed on your Linux OS, you can launch it by keying in the following command on your Linux terminal: $ htop To install Htop on a Linux operating system distribution of your choice, reference one of the following installation commands: $ sudo apt-get install htop
#Linux terminal process monitor how to
How to Install and Use Htop in Linux System While top focuses on the display of resource-intensive processes, Htop will list and display all available and running processes on your Linux system. Htop’s flexible interpretation of system processes makes it a better candidate to top command (an older process viewer and manager for Linux). It is a powerful process viewer, process manager, and system control Linux tool that continuously reveals an updated list of all running processes and their associated resources and activities in relation to an active and authenticated Linux user.
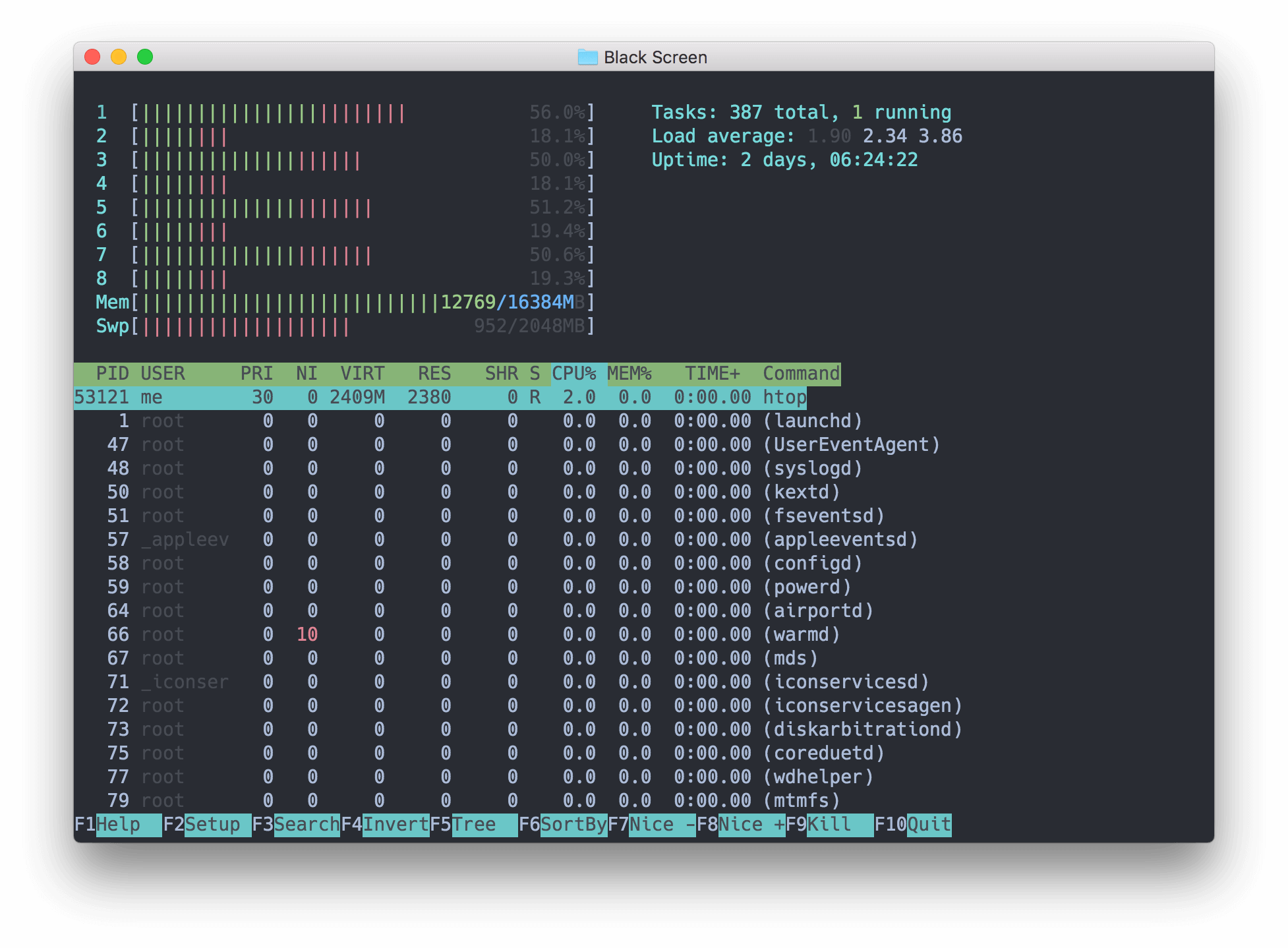
Solving the above-mentioned process communication and deadlock handling issues is possible through the Htop process viewer.

This situation leads to several highly prioritized processes existing in an indefinite paused state.
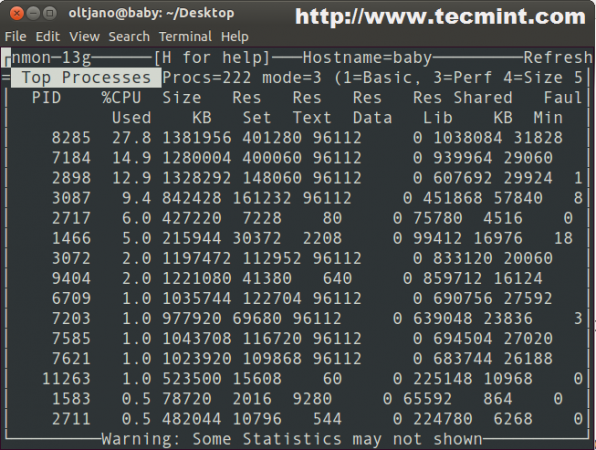
A PID or Process ID uniquely identifies each process on your operating system. This program execution trail that translates to a process is associated with inputs and outputs.Īvailable system resources/services are often utilized by the processes as mandatory inputs to achieve a targeted system objective (output). A program only becomes a process when it starts running/executing. In a Linux operating system environment, a process is defined as a program in execution or one that is already running.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
